Systems manager: Systems Manager: 7 Ultimate Power Roles Revealed
If you’ve ever wondered who keeps the digital backbone of a company running smoothly, meet the systems manager — the unsung hero of modern tech operations. This role blends technical mastery with leadership, ensuring that every system, from servers to software, functions flawlessly.
What Is a Systems Manager? Defining the Role

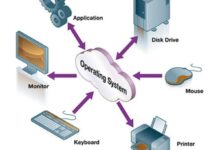
The term systems manager might sound technical, but its impact spans across departments, industries, and digital ecosystems. At its core, a systems manager is responsible for overseeing the design, implementation, maintenance, and optimization of an organization’s IT infrastructure. This includes hardware, software, networks, and cloud environments.
Core Responsibilities of a Systems Manager
A systems manager wears many hats. Their day-to-day tasks are as diverse as the systems they manage. Key responsibilities include:
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Monitoring system performance and ensuring uptime
- Planning and executing system upgrades and patches
- Managing user access and security protocols
- Coordinating with developers, network engineers, and cybersecurity teams
- Documenting system configurations and troubleshooting procedures
These tasks ensure that the organization’s technology runs efficiently and securely. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, demand for IT infrastructure professionals, including systems managers, is projected to grow 4% from 2022 to 2032, faster than the average for all occupations.
How It Differs From Similar Roles
It’s easy to confuse a systems manager with a network administrator or IT director. However, the systems manager role is more holistic. While a network administrator focuses on connectivity and data flow, a systems manager oversees the entire ecosystem — including servers, operating systems, virtualization, automation tools, and integration with business applications.
“A systems manager doesn’t just fix problems — they anticipate them.” — TechOps Lead, Google Cloud
Unlike a CIO or CTO, who operate at a strategic level, systems managers are hands-on leaders who implement and maintain the technology that supports high-level strategies.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Key Skills Every Systems Manager Must Have
To excel as a systems manager, one must blend technical expertise with soft skills. The role demands both depth and breadth of knowledge.
Technical Proficiency
Systems managers must be fluent in multiple operating systems (Linux, Windows, macOS), virtualization platforms (VMware, Hyper-V), and cloud services (AWS, Azure, GCP). They should also understand scripting languages like Python, Bash, or PowerShell to automate repetitive tasks.
- Server administration (physical and virtual)
- Cloud infrastructure management
- Containerization (Docker, Kubernetes)
- Monitoring tools (Nagios, Zabbix, Prometheus)
- Disaster recovery and backup solutions
For example, a systems manager at a fintech startup might use AWS to deploy scalable microservices while ensuring compliance with financial regulations like PCI-DSS.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Problem-Solving and Analytical Thinking
When a server crashes at 2 a.m., the systems manager is the first responder. They must quickly analyze logs, identify root causes, and restore services with minimal downtime. This requires sharp analytical skills and the ability to remain calm under pressure.
Tools like Splunk or ELK Stack help in log analysis, but the real value lies in the manager’s ability to interpret data and make informed decisions. A study by IBM’s Institute for Business Value found that organizations with skilled systems managers experience 40% less unplanned downtime.
Systems Manager vs. IT Manager: What’s the Difference?
While both roles fall under the IT umbrella, their focus areas differ significantly. Understanding these distinctions helps organizations assign the right responsibilities and build effective teams.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Scope of Responsibility
An IT manager typically oversees people, budgets, and projects. Their role is more administrative, focusing on team leadership, vendor management, and aligning IT goals with business objectives. In contrast, a systems manager dives deep into the technical architecture, ensuring that servers, databases, and applications run optimally.
- IT Manager: People, processes, budgets
- Systems Manager: Systems, performance, automation
Think of the IT manager as the conductor of an orchestra, while the systems manager is the lead technician ensuring every instrument is tuned and functioning.
Career Path and Reporting Structure
In many organizations, the systems manager reports to the IT manager or CIO. However, in tech-heavy companies like SaaS providers or data centers, the systems manager may have equal standing due to their critical role in system reliability.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
According to Gartner, the line between technical and managerial roles is blurring, with systems managers increasingly taking on hybrid roles that combine hands-on work with team leadership.
The Evolution of the Systems Manager Role
The role of the systems manager has transformed dramatically over the past two decades. What once involved managing on-premise servers now includes overseeing distributed cloud environments, DevOps pipelines, and AI-driven monitoring tools.
From On-Premise to Cloud-Centric
In the early 2000s, systems managers spent most of their time in server rooms, racking and stacking physical machines. Today, the focus has shifted to cloud platforms. A modern systems manager must understand Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools like Terraform or Ansible, and be proficient in managing cloud resources across multiple providers.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Legacy systems: Physical servers, local backups, manual updates
- Modern systems: Cloud VMs, automated scaling, CI/CD integration
- Future trends: Serverless computing, edge computing, AI-driven operations
This shift has increased the strategic importance of the systems manager, as they now play a key role in digital transformation initiatives.
Integration with DevOps and SRE
The rise of DevOps and Site Reliability Engineering (SRE) has redefined how systems are managed. Systems managers are no longer isolated from development teams. Instead, they collaborate closely to ensure smooth deployments, rapid incident response, and continuous improvement.
For instance, a systems manager might work with developers to containerize an application using Docker and deploy it via Kubernetes, ensuring scalability and resilience. This collaboration reduces silos and accelerates innovation.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
“The best systems managers are bridge-builders between development and operations.” — DevOps Research & Assessment (DORA)
How to Become a Systems Manager: Education and Certifications
Becoming a systems manager requires a mix of formal education, hands-on experience, and industry-recognized certifications.
Recommended Educational Background
Most systems managers hold a bachelor’s degree in computer science, information technology, or a related field. Coursework in networking, operating systems, and database management provides a strong foundation.
- Computer Science (B.Sc.)
- Information Systems (B.A.)
- Engineering with IT focus
While a degree is valuable, many employers prioritize practical skills and experience. Bootcamps, online courses, and self-taught expertise can also lead to a successful career in systems management.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Top Certifications for Career Advancement
Certifications validate expertise and open doors to higher-paying roles. The most respected certifications for systems managers include:
- CompTIA Server+: Covers server hardware, software, and disaster recovery
- Microsoft Certified: Azure Administrator Associate: Focuses on cloud infrastructure management
- Red Hat Certified Engineer (RHCE): For Linux system administration
- AWS Certified SysOps Administrator – Associate: Validates cloud operations skills
- Google Professional Cloud Architect: For multi-cloud environments
According to CompTIA’s 2023 IT Industry Outlook, certified professionals earn up to 20% more than their non-certified peers.
Day in the Life of a Systems Manager
There’s no such thing as a “typical” day for a systems manager, but certain patterns emerge based on industry, company size, and technology stack.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Morning Routine: Monitoring and Maintenance
The day often starts with checking system dashboards. Tools like Datadog, New Relic, or Grafana provide real-time insights into server health, network traffic, and application performance.
- Review overnight alerts and resolve any incidents
- Apply security patches or system updates
- Verify backup integrity and replication status
This proactive approach prevents small issues from escalating into major outages.
Afternoon Tasks: Projects and Collaboration
After the morning checks, systems managers often shift to project work. This could include:
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Planning a migration to the cloud
- Optimizing database performance
- Training junior team members
- Attending cross-functional meetings with security or development teams
Collaboration is key. A systems manager at a healthcare provider, for example, might work with compliance officers to ensure HIPAA requirements are met in their system configurations.
Challenges Faced by Systems Managers Today
Despite the rewards, the role comes with significant challenges that test even the most experienced professionals.
Managing Complexity in Hybrid Environments
Many organizations operate in hybrid environments — a mix of on-premise servers, private clouds, and public cloud services. This complexity makes monitoring, security, and troubleshooting more difficult.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
- Inconsistent tooling across platforms
- Data sovereignty and compliance issues
- Integration challenges between legacy and modern systems
A systems manager must navigate these complexities while maintaining performance and security.
Keeping Up with Rapid Technological Change
Technology evolves at breakneck speed. New tools, frameworks, and security threats emerge constantly. Systems managers must engage in continuous learning to stay relevant.
For example, the rise of AI-powered operations (AIOps) means managers must now understand machine learning models that predict system failures. Platforms like Moogsoft or Dynatrace use AI to analyze logs and detect anomalies — skills that weren’t required just five years ago.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
“The half-life of technical skills is now less than 2.5 years.” — World Economic Forum
Future Trends Shaping the Systems Manager Role
The future of systems management is being shaped by automation, artificial intelligence, and decentralized computing.
Automation and AI-Driven Operations
Manual system administration is becoming obsolete. Tools like Ansible, Puppet, and Chef automate configuration management, while AI-driven platforms predict failures before they occur.
- Self-healing systems that automatically restart failed services
- Predictive scaling based on usage patterns
- Natural language interfaces for system queries (e.g., “Show me all servers with high CPU”)
Systems managers will increasingly act as supervisors of automated systems rather than direct operators.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
The Rise of Edge Computing and IoT
With the growth of IoT devices and 5G networks, data is being processed closer to the source. This shift to edge computing requires systems managers to manage distributed systems across geographically dispersed locations.
For example, a logistics company might deploy edge servers in delivery trucks to process GPS and sensor data in real time. The systems manager must ensure these edge nodes are secure, updated, and synchronized with central systems.
What does a systems manager do?
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
A systems manager oversees the design, implementation, and maintenance of an organization’s IT infrastructure. This includes servers, networks, cloud services, and security protocols. They ensure systems run efficiently, securely, and with minimal downtime.
What skills are needed to become a systems manager?
Key skills include proficiency in operating systems (Linux/Windows), cloud platforms (AWS/Azure), scripting (Python/Bash), and monitoring tools. Soft skills like problem-solving, communication, and project management are also essential.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Is a degree required to be a systems manager?
While many systems managers hold a bachelor’s degree in computer science or IT, it’s not always mandatory. Certifications (like AWS or RHCE) and hands-on experience can be equally valuable, especially in tech-forward companies.
How much does a systems manager earn?
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, the median annual wage for computer and information systems managers was $164,000 in 2022. Salaries vary by location, industry, and experience level.
What’s the difference between a systems manager and a network administrator?
A network administrator focuses on connectivity, routing, and data flow. A systems manager has a broader scope, managing servers, operating systems, cloud infrastructure, and integration with business applications.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
The role of a systems manager is more critical than ever in our digital-first world. From ensuring uptime to driving innovation, they are the backbone of modern IT operations. As technology evolves, so too will the systems manager — adapting to cloud, AI, and edge computing with skill and precision. Whether you’re aspiring to become one or looking to hire a top-tier professional, understanding this role’s depth and impact is essential for success in the tech landscape.
systems manager – Systems manager menjadi aspek penting yang dibahas di sini.
Further Reading: