System Backup: 7 Ultimate Strategies for Total Data Protection
In today’s digital world, losing critical data can be catastrophic. A solid system backup isn’t just smart—it’s essential for survival. Discover the ultimate strategies to protect your data like a pro.
What Is a System Backup and Why It Matters

A system backup refers to the process of copying and archiving computer data so it can be restored in the event of data loss. This loss could stem from hardware failure, software corruption, cyberattacks, or human error. The importance of a reliable system backup cannot be overstated—especially in an era where data is often more valuable than physical assets.
Defining System Backup
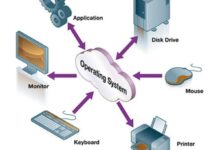
At its core, a system backup involves creating a duplicate of your operating system, applications, settings, and personal files. This copy can reside on external drives, network-attached storage (NAS), or cloud platforms. Unlike file-level backups, which only save individual documents, a full system backup captures the entire state of your computer at a given moment.
- Includes OS, installed programs, user profiles, and system settings
- Enables complete system restoration after failure
- Can be automated or performed manually
According to the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), organizations that lack proper backup protocols are 3.5 times more likely to suffer irreversible data loss after a cyber incident (NIST SP 800-34 Rev. 1).
Common Causes of Data Loss
Data doesn’t vanish without cause. Understanding the root causes helps emphasize why a robust system backup strategy is non-negotiable.
Hardware Failure: Hard drives fail.SSDs wear out.RAID arrays aren’t foolproof.A 2023 Backblaze report showed that 1.8% of hard drives fail annually, with higher rates after the third year.Malware and Ransomware: Cybercriminals encrypt or delete data, demanding payment.The 2023 Verizon Data Breach Investigations Report found that 71% of breaches were financially motivated, with ransomware attacks increasing by 15% year-over-year.Human Error: Accidental deletion, formatting, or overwriting is surprisingly common..
A University of Cambridge study estimated that 23% of data loss incidents stem from user mistakes.Natural Disasters: Fires, floods, and power surges can destroy physical infrastructure.Offsite or cloud-based system backup solutions are critical here.”Data is the new oil, but unlike oil, it doesn’t run out.However, it can be lost forever if not properly backed up.” — Clive Humby, Mathematician and Data Science PioneerTypes of System Backup: Full, Incremental, and DifferentialNot all system backup methods are created equal.Choosing the right type depends on your recovery time objectives (RTO), storage capacity, and frequency needs.Let’s break down the three primary types..
Full System Backup
A full system backup copies every file, folder, application, and system setting on your device. It’s the most comprehensive method and serves as the foundation for other backup types.
- Pros: Complete restoration capability, simple recovery process
- Cons: Time-consuming, requires significant storage space
- Best for: Weekly or monthly backups, initial baseline copies
For example, Windows users can use System Image Backup via Control Panel to create a full system backup on an external drive. Mac users can rely on Time Machine for similar functionality.
Incremental System Backup
After an initial full backup, incremental backups only save data that has changed since the last backup—whether full or incremental.
- Pros: Fast, efficient use of storage, ideal for daily use
- Cons: Longer recovery time (requires full + all incrementals)
- Best for: Environments with frequent data changes and limited bandwidth
Tools like Acronis True Image and MiniTool ShadowMaker support incremental system backup scheduling.
Differential System Backup
Differential backups capture all changes made since the last full backup. Unlike incremental, they don’t reset after each backup.
- Pros: Faster recovery than incremental (only full + latest differential needed)
- Cons: Grows larger over time, consumes more storage
- Best for: Mid-sized businesses needing faster restores than incremental allows
For instance, if you perform a full backup on Sunday, Monday’s differential includes changes from Sunday to Monday. Tuesday’s includes changes from Sunday to Tuesday—making each differential larger.
Best Practices for an Effective System Backup Strategy
Having a backup is good. Having a smart, reliable, and tested system backup strategy is what truly protects you. Here are the best practices every individual and organization should follow.
Follow the 3-2-1 Backup Rule
This golden rule is widely endorsed by IT professionals and cybersecurity experts. It states:
- Keep 3 copies of your data (1 primary + 2 backups)
- Store them on 2 different media (e.g., SSD + cloud)
- Keep 1 copy offsite (e.g., cloud or remote server)
This approach minimizes risk from localized disasters and media failure. For example, if your office burns down, your offsite cloud backup ensures business continuity.
Automate Your System Backup
Manual backups are unreliable. People forget. Automation ensures consistency and timeliness.
- Use built-in tools like Windows Backup and Restore or macOS Time Machine
- Leverage third-party software such as Veeam, EaseUS Todo Backup, or Macrium Reflect
- Schedule backups during off-peak hours to minimize performance impact
Automation also allows for versioning—keeping multiple restore points over time, which is crucial for recovering from ransomware attacks that may go unnoticed for days.
Regularly Test Your Backups
A backup that can’t be restored is no backup at all. Testing ensures integrity and functionality.
- Perform quarterly restore drills
- Verify file accessibility and system bootability
- Document test results and update procedures accordingly
The U.S. Department of Homeland Security recommends testing backups at least twice a year to ensure readiness for cyber incidents (CISA KEV Catalog).
Top Tools and Software for System Backup
Choosing the right tool can make or break your system backup experience. Here’s a breakdown of the most reliable and widely used software across platforms.
Windows: Built-in and Third-Party Options
Windows offers several native tools, but third-party solutions often provide more flexibility and features.
- Windows Backup and Restore (Windows 7/10): Allows system image creation and file history.
- File History: Backs up personal files to an external drive or network location.
- Third-Party Tools: Acronis True Image, Macrium Reflect, and EaseUS Todo Backup offer disk imaging, cloud sync, and bare-metal recovery.
For enterprise environments, Veeam Backup & Replication is a top choice for virtual and physical infrastructure.
macOS: Time Machine and Beyond
Apple’s Time Machine is one of the most user-friendly system backup solutions available.
- Automatically backs up to an external drive or AirPort Time Capsule
- Supports versioning and easy file restoration
- Can restore the entire system from a bootable backup
For advanced users, tools like SuperDuper! and Carbon Copy Cloner offer more granular control and bootable clone creation.
Linux: Command-Line and GUI Solutions
Linux users have powerful, flexible options—many of which are open-source and free.
- rsync: A command-line tool for efficient file synchronization and backup.
- Timeshift: Creates system snapshots for easy rollback (similar to Windows System Restore).
- BorgBackup: Offers deduplication, compression, and encryption for efficient storage.
- Clonezilla: A disk imaging tool for full system backup and deployment.
For enterprise use, Bareos provides scalable, secure backup solutions for large Linux environments.
Cloud-Based System Backup: Pros, Cons, and Top Providers
Cloud-based system backup has revolutionized data protection by offering offsite storage, scalability, and accessibility from anywhere.
Advantages of Cloud Backup
Storing your system backup in the cloud comes with compelling benefits:
- Automatic Sync: Changes are backed up in real-time or on schedule without user intervention.
- Disaster Recovery: Protects against physical damage to local devices.
- Scalability: Pay only for the storage you use, with easy expansion.
- Accessibility: Restore files or systems from any internet-connected device.
Providers like Backblaze and IDrive offer unlimited backup plans starting at under $7/month.
Challenges and Risks
Despite its advantages, cloud-based system backup isn’t without drawbacks:
- Internet Dependency: Slow upload speeds can delay initial backups.
- Security Concerns: Data is stored on third-party servers—encryption is critical.
- Long-Term Costs: While affordable initially, costs can rise with data volume.
- Vendor Lock-In: Migrating large datasets between providers can be complex.
To mitigate risks, always enable end-to-end encryption and use two-factor authentication (2FA) for your cloud accounts.
Top Cloud Backup Services
Here are some of the most trusted cloud-based system backup providers:
- Backblaze: Simple, unlimited backup for personal use. No file size limits.
- IDrive: Offers hybrid cloud and local backup, supports multiple devices.
- Carbonite: Strong focus on business continuity and ransomware protection.
- pCloud: Lifetime plans available, with client-side encryption (pCloud Crypto).
- Google Workspace Backup: For businesses using Google services, third-party tools like Centrify ensure data isn’t lost due to accidental deletion.
“The cloud is not a backup strategy—it’s a storage location. Your strategy must include versioning, encryption, and testing.” — Paul Bischoff, Privacy Advocate at Comparitech
System Backup for Businesses: Scaling for Enterprise Needs
For businesses, system backup isn’t just about data—it’s about continuity, compliance, and reputation. A single outage can cost millions.
Business Continuity and Disaster Recovery (BCDR)
Enterprises must plan for worst-case scenarios. A BCDR plan includes:
- Recovery Time Objective (RTO): How fast systems must be restored.
- Recovery Point Objective (RPO): How much data loss is acceptable (e.g., 1 hour vs. 24 hours).
- Failover systems: Redundant servers that take over during outages.
According to IBM’s Cost of a Data Breach Report 2023, organizations with automated response systems saved $1.76 million on average per breach.
Compliance and Legal Requirements
Many industries are legally required to maintain system backups.
- Healthcare (HIPAA): Requires secure, encrypted backups of patient data.
- Finance (SOX, GLBA): Mandates data retention and audit trails.
- GDPR (EU): Requires data protection and the right to data portability.
Failure to comply can result in fines, lawsuits, and loss of customer trust.
Centralized Backup Management
Large organizations need centralized control over backup operations.
- Tools like Veeam, Commvault, and Rubrik offer dashboards for monitoring all backups.
- Role-based access ensures only authorized personnel can manage or restore data.
- Integration with SIEM (Security Information and Event Management) systems enhances threat detection.
Centralized logging also helps during audits by providing a clear record of backup activities.
Emerging Trends in System Backup Technology
The world of system backup is evolving rapidly. New technologies are making backups faster, smarter, and more secure.
AI-Powered Backup Solutions
Artificial intelligence is being used to predict failures and optimize backup schedules.
- AI analyzes usage patterns to determine optimal backup times.
- Machine learning detects anomalies that may indicate ransomware.
- Predictive analytics can warn of impending hardware failure before it happens.
For example, Cohesity uses AI to streamline data management across hybrid environments.
Immutable Backups and Air-Gapped Storage
To combat ransomware, many organizations are adopting immutable backups—copies that cannot be altered or deleted for a set period.
- Immutable backups are often stored in air-gapped systems (physically disconnected from networks).
- Amazon S3 Glacier Vault Lock and Azure Immutable Blob Storage support this model.
- WORM (Write Once, Read Many) technology ensures data integrity.
According to a 2023 report by Cybersecurity Ventures, immutable backups reduced ransomware recovery costs by 68%.
Blockchain for Backup Integrity
While still in early stages, blockchain is being explored to verify backup authenticity.
- Each backup is hashed and recorded on a blockchain ledger.
- Ensures no tampering has occurred between creation and restoration.
- Useful for legal, financial, and government sectors requiring audit-proof records.
Projects like Storj and Sia are pioneering decentralized cloud storage with blockchain verification.
What is the difference between a system backup and a file backup?
A system backup includes the entire operating system, applications, settings, and files, allowing for full system restoration. A file backup only saves selected documents and folders, not the OS or programs.
How often should I perform a system backup?
For personal users, weekly full backups with daily incremental ones are recommended. Businesses should back up critical systems daily or in real-time, depending on RPO requirements.
Can I restore a system backup to a different computer?
Yes, but hardware differences may cause driver conflicts. Use tools that support bare-metal recovery for smoother transitions between machines.
Is cloud backup safe for system images?
Yes, if the provider uses strong encryption (AES-256) and allows client-side encryption. Always verify the provider’s security certifications (e.g., SOC 2, ISO 27001).
What is bare-metal recovery?
Bare-metal recovery allows you to restore a complete system backup to a new or wiped machine, even without an OS installed. It’s essential for disaster recovery scenarios.
A robust system backup strategy is no longer optional—it’s a fundamental pillar of digital resilience. Whether you’re an individual protecting family photos or a corporation safeguarding customer data, the principles remain the same: automate, diversify, test, and secure. By following the 3-2-1 rule, leveraging modern tools, and staying ahead of emerging threats like ransomware, you can ensure your data survives any disaster. The cost of backup is minimal compared to the cost of loss. Start today—because when data disappears, it’s too late to regret not having a plan.
Further Reading: